Teaching
Lectures
- Real-time Concepts for Embedded Systems (WS2019/20), University of Sttutgart, Germany (Below are more details about the course)
- Real-time Concepts for Embedded Systems (WS2018/19), University of Sttutgart, Germany
- Distributed Systems 2018/19 (Jointly with Prof. Dr. Kurt Rothermel), University of Sttutgart, Germany
- Distributed Systems 2017/18 (Jointly with Prof. Dr. Kurt Rothermel), University of Sttutgart, Germany
- Distributed Systems 2016/17 (Jointly with Prof. Dr. Kurt Rothermel), University of Sttutgart, Germany
- Digital signal processing, communication theory, integrated circuits, electrical circuits (2011-2012), Port Said University, Egypt
- Solid-state devices, electronic circuits, digital circuits, digital communication, satellite communication, and microprocessor design (2009-2011), Suez Canal University, Egypt
Seminars
- Advanced Topics in Distributed Systems, Smart Microsystems in Autonomous Driving Applications (2017/18), University of Sttutgart, Germany (Below are more details about the seminar)
- Advanced Topics in Distributed Systems, Smart Microsystems in Autonomous Driving Applications (2018/19), University of Sttutgart, Germany
- Security in mobile-based services (2017/18), University of Sttutgart, Germany
Real-time Cocepts for Embeeded Systems
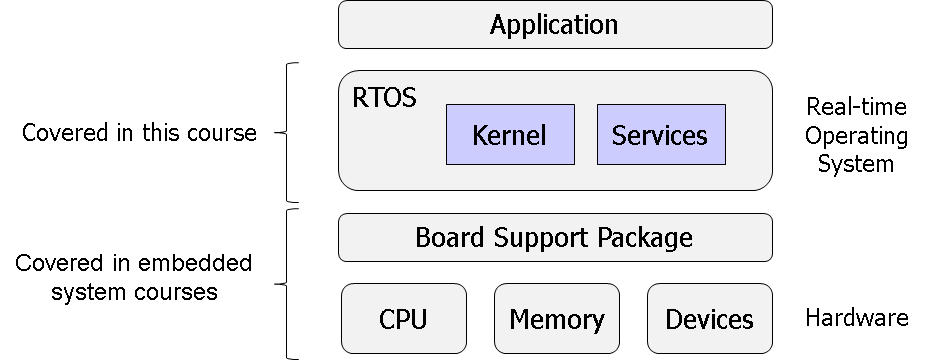
Many of nowadays-embedded systems are designed to work in real time, e.g., automotive systems, avionics, industrial processes control. The goal of the lecture is to give an understanding of fundamental concepts used in modern real-time operating systems (RTOS). The participants will learn main concepts behind real-time systems such as their characteristics and time constraints. Moreover, several academic and industrial examples of RTOS will be given as use cases. Additionally, the course introduces the various components of a typical RTOS including the kernel and the other provided services such as file management and I/O management. The participants also will learn several algorithms in the realm of tasks scheduling, inter-tasks communication, synchronization, and resources access management. The contents of this course include:
- Fundamentals of real-time Systems
- Real-time Scheduling
- Time Management
- Resource Access Control
- Inter-task communication
- Memory Management
- File I/O Management
Advanced Topics in Distributed Systems: Smart Microsystems in Autonomous Driving Applications
Internet of Things (IoT) describes a general concept for the ability of items in the physical world to sense and collect data from the surroundings, and then share that data across the Internet where it can be processed and utilized for various interesting purposes. These capabilities have certainly opened the door for several applications. Autonomous driving is one of these applications in which the IoT concepts are used to augment the vehicles’ intelligence. In this context, advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) feature an increasing degree of automation towards the goal of fully automated driving for safe and comfortable travel. This trend promises a reduction in the number and severity of traffic accidents, of traffic congestions as well as fuel consumption, thus leading to resource-saving mobility. Accordingly, several industry giants, such as Daimler, BMW, Bosch, Tesla, Google, and Uber, are currently competing to release the first commercial fully-autonomous vehicle.
In general, ADAS is an interdisciplinary field that spans across all the levels of functional hierarchy, from hardware fault tolerance, to advanced machine learning, to cooperating with conventional vehicles, to validating systems for operation in highly unstructured environments. To design such systems, several sensors, such as radar, video cameras, LiDAR, and ultrasonic, generate continuous stream of data processed by an array of processing units. In this seminar, we cover several important components of the autonomous driving system. The discussed areas includes, but not limited to:
- Sensing technologies and sensor fusion protocols
- Automotive networking protocols (CAN, Automotive Ethernet, TSN, LIN)
- Software standards (RTOS, AUTOSAR, SPICE)
- Multiprocessor real-time scheduling
- Resilient machine learning algorithms
- Driver assistance and vehicle automation (SLAM, safety, pedestrians detection)
- Security (intrusion detection, blockchain)